EMu supports numerous image, audio and video formats, as well as the EXIF, IPTC and XMP metadata standards.
The Multimedia module is also compliant with the Dublin Core Metadata standard.
Read on for details about:
The Multimedia repository supports all media types, including:
- Image, video, audio
- Word processing documents, spreadsheets, presentations
- Any online or off-line resource
- All Dublin Core Metadata fields
Images
EMu uses the open source ImageMagick libraries, with support for over 100 image file formats. By default, EMu handles the following formats:
- BMP - Microsoft Windows Bitmap Image
- DCX - ZSoft IBM PC multi-page Paintbrush
- GIF - CompuServe Graphics Interchange Format
- JP2 - JPEG 2000
- JPEG - Joint Photographic Experts Group
- PCD - Photo CD
- PCX - ZSoft IBM PC Paintbrush
- PNG - Portable Network Graphics
- TGA - Truevision Targa Image
- TIFF - Tagged Image File Format
EMu will also automatically include any image formats registered by other applications installed on your computer.
Two Registry entries provide control over which formats are used within an institution (Include and Exclude)
Audio and Video support
The audio and video libraries used by EMu provide support for a larger range of formats. Supported Audio formats are:
- AIFF - Audio Interchange File Format
- AU - Audio File Format
- MIDI - Musical Instrument Digital Interface
- MP3 - MPEG Audio Stream, Layer III
- RMI - MIDI in RIFF File Format
- SND - Sound File Format
- WAV - Waveform Audio
- WMA - Windows Media Audio File
Supported Video formats are:
- ASF - Advanced Streaming Format
- AVI - Audio Video Interleave File
- M1V - MPEG-1 Video File
- M2V - MPEG-2 Video File
- MOD - JVC Everio GZ-MG20U Digital Video File
- MPEG - MPEG 1 System Stream
- WMV - Windows Media File
EMu detects all audio and video formats registered with Windows and makes them available.
The Metadata|Extract Registry entry controls what metadata is copied into EMu.
Whenever an image is derived from a master image in EMu (i.e. a different resolution of the master image), it is possible to copy some or all of the master image's metadata to the derived image. The Metadata|Embed Registry Entry controls what metadata is copied from the master image to the derived image(s).
EMu supports three metadata standards, with a tab provided for each in the Multimedia module:
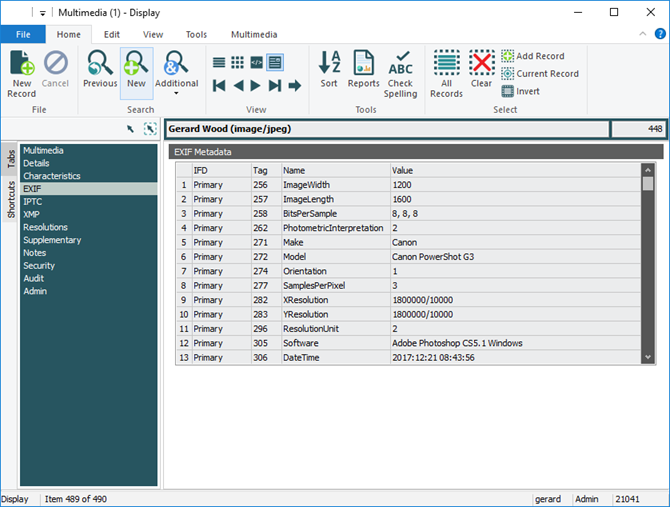
- EXIF - Exchangeable Image File Format (Version 2.2, April 2002):
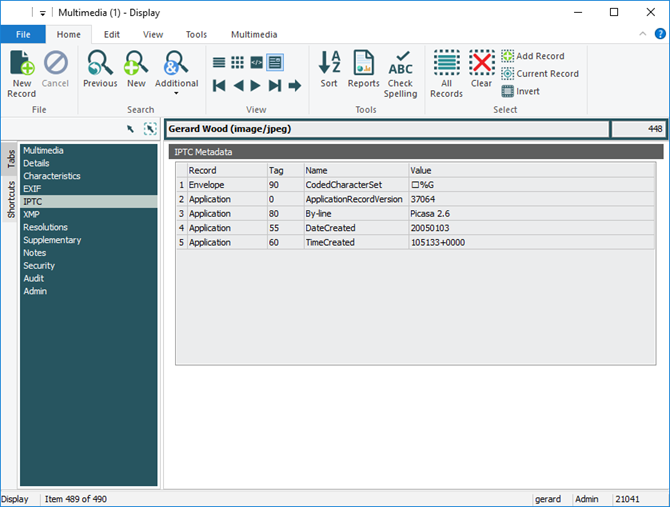
- IPTC - International Press Telecommunications Council (IIM Version 4.1, July 1999):
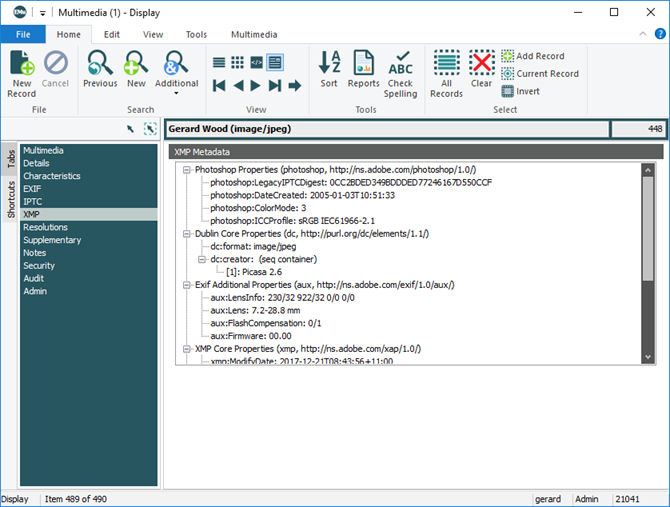
- XMP - Extensible Metadata Platform (Revision September 2005):
When an image is added to the Multimedia module, metadata is extracted from the file and stored on the appropriate tab:
- EXIF supports jpeg and tiff formats
- IPTC supports jpeg, tiff, pict, ps and psd formats
- XMP supports jpeg and tiff formats
The Multimedia module is compliant with the Dublin Core Metadata standard version 1.1. The Dublin Core Metadata standard consists of fifteen fields that describe a multimedia resource:
|
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Title |
A name given to the resource. |
|
Creator |
An entity primarily responsible for making the content of the resource. Examples include a person, an organization, or a service. |
|
Subject |
The topic of the content of the resource. Typically, a Subject will be expressed as key words, key phrases or classification codes that describe a topic of the resource. |
|
Description |
A description of the multimedia resource. Description may include but is not limited to: an abstract, table of contents, reference to a graphical representation of content or a free-text account of the content. |
|
Publisher |
An entity responsible for making the resource available. |
|
Contributor |
An entity responsible for making contributions to the content of the resource. |
|
Date |
A date associated with an event in the life cycle of the resource. |
|
Type |
The type of multimedia resource, e.g. image, video, document, etc. |
|
Format |
The file type / format of the multimedia resource, e.g. bmp, jpg, mov, doc, etc. |
|
Identifier |
An unambiguous reference to the resource within a given context. Examples include the Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) (including the Uniform Resource Locater (URL)), the Digital Object Identifier (DOI) and the International Standard Book Number (ISBN). |
|
Source |
A reference to a resource from which the present resource is derived. |
|
Language |
A language of the intellectual content of the resource. |
|
Relation |
A reference to a related resource. |
|
Coverage |
The extent or scope of the content of the resource. |
|
Rights |
Information about rights held in and over the resource. |